Introduction
The healthcare industry is undergoing a transformative shift with the integration of blockchain technology into its supply chains. Blockchain, originally developed as the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies, offers a decentralized and secure framework for managing and tracking the flow of goods and information. In the realm of healthcare supply chains, blockchain is proving to be a powerful tool, enhancing transparency, traceability, and security. This article explores the profound impact of blockchain on healthcare supply chains, examining the benefits, challenges, and future possibilities.
Understanding Healthcare Supply Chains
Complexity and Challenges
Healthcare supply chains are intricate systems involving the production, distribution, and delivery of pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and other critical supplies. The complexity of these supply chains poses challenges such as counterfeiting, inefficiencies, and difficulties in tracing the origins and movement of products.
Importance of Traceability
Traceability is a critical factor in healthcare supply chains, especially considering the stringent regulatory requirements and the need to ensure the authenticity and quality of medical products. The ability to trace the journey of each product from manufacturing to delivery is essential for safeguarding patient safety and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Blockchain’s Role in Healthcare Supply Chains
Transparency and Traceability
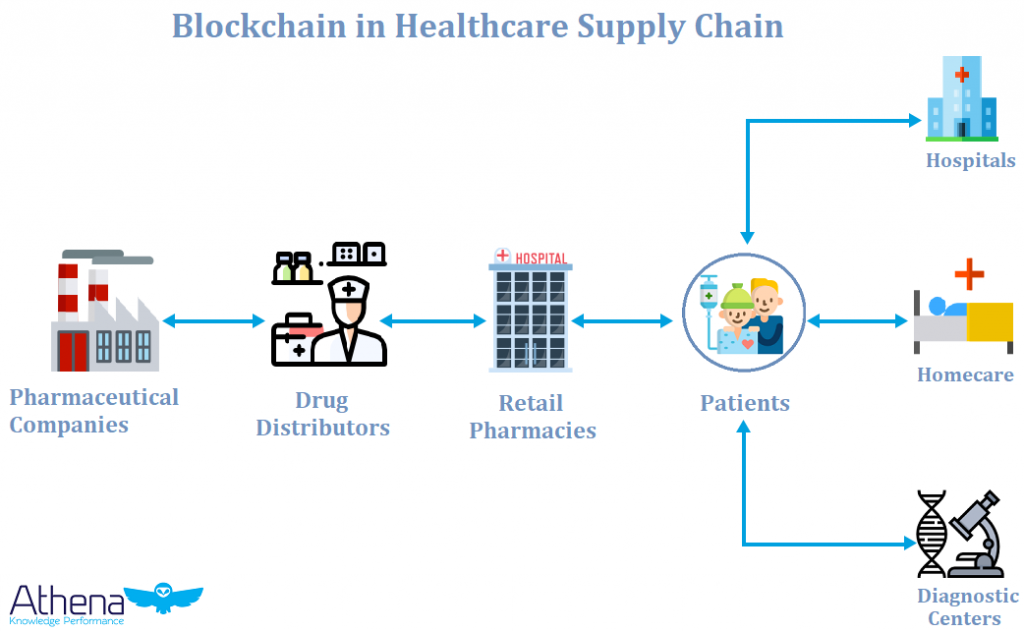
Blockchain introduces transparency and traceability into healthcare supply chains by creating an immutable and decentralized ledger. Each transaction or movement of a product is recorded in a secure and transparent manner, providing stakeholders with real-time visibility into the entire supply chain. This transparency reduces the risk of errors, fraud, and unauthorized alterations.
Enhanced Security with Smart Contracts
Blockchain utilizes smart contracts, self-executing agreements with predefined rules, to automate and secure various processes in healthcare supply chains. Smart contracts facilitate trust among stakeholders, ensuring that contractual obligations are met without the need for intermediaries. This enhances the security and efficiency of transactions throughout the supply chain.
Read More:
Real-time Monitoring and Data Integrity
The decentralized nature of blockchain enables real-time monitoring of the supply chain, allowing stakeholders to access accurate and up-to-date information. Data stored on the blockchain is cryptographically secured, ensuring the integrity of information. This reduces the likelihood of errors, inaccuracies, or malicious tampering that can compromise the quality and safety of healthcare products.
Benefits of Blockchain in Healthcare Supply Chains
Counterfeit Prevention
Counterfeit drugs pose a significant threat to public health. Blockchain’s ability to provide an unforgeable record of each pharmaceutical product’s journey through the supply chain helps prevent the entry of counterfeit drugs. Patients and healthcare providers can verify the authenticity of medications, ensuring that they receive genuine and safe products.
Efficient Recall Management
In cases of product recalls, blockchain streamlines the process by quickly identifying affected batches. This rapid identification reduces the time it takes to initiate recalls, minimizing the potential harm to patients. Stakeholders can trace the origin and distribution of affected products with precision, enhancing the effectiveness of recall management.
Regulatory Compliance
Blockchain facilitates regulatory compliance by providing a transparent and auditable record of activities within the supply chain. This transparency simplifies the process of demonstrating adherence to regulatory standards and requirements. As a result, healthcare organizations can navigate complex regulatory landscapes with greater ease.
Challenges and Considerations
Integration with Existing Systems
One of the challenges in implementing blockchain in healthcare supply chains is integrating the technology with existing systems. Healthcare organizations often use diverse and legacy systems, and ensuring seamless interoperability with blockchain solutions requires careful planning and technical expertise.
Standardization and Collaboration
The success of blockchain in healthcare supply chains relies on industry-wide standardization and collaboration. Establishing common protocols and standards is crucial for ensuring that different stakeholders can effectively share and access information on the blockchain. Collaboration among manufacturers, distributors, regulators, and healthcare providers is essential for creating a unified blockchain ecosystem.
Future Possibilities and Innovations
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The integration of blockchain with the Internet of Things (IoT) holds promise for healthcare supply chains. IoT devices can provide real-time data on the condition and location of products, and blockchain ensures the secure and transparent storage of this information. This synergy enhances the overall efficiency and accuracy of supply chain management.
Advanced Analytics and Predictive Insights
Blockchain’s ability to securely store and share data sets the stage for advanced analytics and predictive insights. By leveraging the wealth of data on the blockchain, healthcare organizations can gain valuable insights into supply chain trends, demand patterns, and potential risks. This data-driven approach enables proactive decision-making and optimization of supply chain processes.
Conclusion
The integration of blockchain technology into healthcare supply chains represents a transformative leap toward a more transparent, secure, and efficient ecosystem. From preventing counterfeits to streamlining recall processes and ensuring regulatory compliance, blockchain brings a host of benefits to the healthcare industry. While challenges such as integration and standardization must be addressed, the ongoing innovations and collaborations in this space point toward a future where blockchain plays a central role in safeguarding the integrity of healthcare supply chains for the benefit of patients worldwide.