This comprehensive introduction to PCB assembly will teach you the basics of the process and help you assemble your circuit boards.
1. Introduction to PCB Assembly
When it comes to electronics, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are one of the most important components. They provide support and connect electronic components using conductive tracks, pads and other features etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate.
PCB assembly is the process of connecting electronic components to a PCB. This can be done by hand, using a soldering iron, or by machine, using an automated pick-and-place machine. The assembly process can be further divided into two main sub-processes: surface-mount assembly and through-hole assembly.
Surface-mount assembly is the process of mounting components onto the surface of a PCB. This is done by soldering the leads of the components to the exposed pads on the PCB. Surface-mount assembly is the preferred method for assembling modern PCBs, as it is faster and more accurate than through-hole assembly.
Through-hole assembly is the process of mounting components onto a PCB by inserting their leads through holes in the PCB and soldering them in place on the other side. Through-hole assembly is not as common as surface-mount assembly, but is still used for some types of PCBs.
Once the components have been assembled onto the PCB, the assembly process is complete. The PCB can then be tested to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
2. The Components of a PCB Assembly
When it comes to printed circuit board (PCB) assembly, there are three main components that are typically used: the printed circuit board itself, the electronic components, and the assembly tools and materials. Let’s take a closer look at each of these components.
The Printed Circuit Board
The printed circuit board, or PCB, is the foundation of any PCB assembly. It is a thin, flat piece of insulating material (usually fiberglass, plastic, or metal) that has a thin layer of metal (usually copper) bonded to one or both sides. This metal layer is etched with a pattern of conductive traces that connect the various electronic components mounted on the board.
The Electronic Components
The electronic components are the active and passive components that are mounted on the PCB. These components include ICs, transistors, diodes, capacitors, resistors, and inductors. They are typically mounted using surface-mount technology (SMT) or through-hole technology (THT).
The Assembly Tools and Materials
The assembly tools and materials are used to assemble the PCB and electronic components. These include soldering irons, solder, flux, PCB files, and desoldering tools.
3. The Steps in a PCB Assembly Process
PCB assembly is the process of connecting electronic components to a printed circuit board (PCB) to create an electronic device. The assembly process begins with the placement of components on the PCB and ends with the soldering of those components to the board.
There are three main steps in the PCB assembly process: component placement, soldering, and inspection.
- Component Placement
The first step in PCB assembly is component placement. This is the process of positioning and attaching components to the PCB. Components are typically placed on the PCB using a pick-and-place machine, which positions and places the components on the PCB according to a set of coordinates.
- Soldering
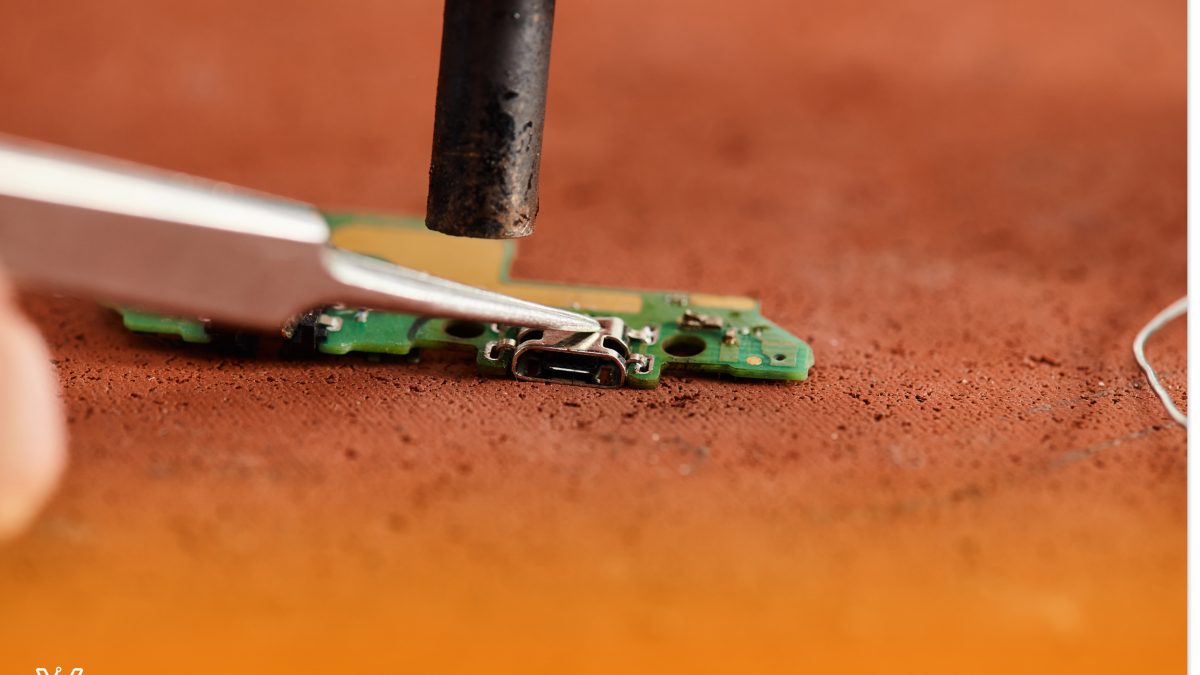
The second step in PCB assembly is soldering. This is the process of connecting the components to the PCB using solder. Solder is a metal that melts at a low temperature and can be used to connect two pieces of metal together.
- Inspection
The third and final step in PCB assembly is inspection. This is the process of checking the PCB assembly for defects. Defects can be found during any of the three steps in the assembly process, but inspection is typically done after the soldering step.
4. The Different Types of PCB Assembly
As the world of electronics gets more and more complex, the need for printed circuit boards (PCBs) becomes more and more important. Printed circuit boards are used to connect electronic components and are found in everything from cell phones to computers.
There are four different types of PCBs: multilayer, rigid-flex, rigid, and flexible.
Multilayer PCBs are the most complex type of PCB. They have multiple layers of circuits, which are connected by vias (small holes that go through the PCB). Multilayer PCBs are used in applications where there is a lot of data transfer, such as in computers.
Rigid-flex PCBs are a type of PCB that is both rigid and flexible. They have a rigid layer and a flexible layer, which are connected by vias. Rigid-flex PCBs are used in applications where there is a need for flexibility, such as in cell phones.
Rigid PCBs are the most common type of PCB. They are made of a single layer of circuits that are connected together. Rigid PCBs are used in a variety of applications, such as in calculators.
Flexible PCBs are made of a thin layer of circuits that are connected together. Flexible PCBs are used in applications where there is a need for flexibility, such as in cell phones.
5. The Benefits of PCB Assembly
We often get asked what the benefits of PCB assembly are. Here are five of the most important benefits:
- Increased Efficiency
With PCB assembly, you can increase the efficiency of your manufacturing process. This is because all of the components are placed on the board in the correct orientation and order, so you can simply start soldering them in place. This can save you a lot of time and effort, as you won’t need to fiddle around with each individual component.
- Improved Quality
Another benefit of PCB assembly is that it can improve the quality of your finished product. This is because all of the components will be placed in the correct orientation and order, so there is less chance of human error. This can lead to a more reliable and durable product.
- Reduced Costs
Another benefit of PCB assembly is that it can help to reduce the costs of your manufacturing process. This is because you won’t need to purchase or store individual components, as they will all be supplied on the PCB. This can save you a lot of money in the long run.
- Increased Speed
Another benefit of PCB assembly is that it can help to increase the speed of your manufacturing process. This is because all of the components are placed on the board in the correct orientation and order, so you can simply start soldering them in place. This can save you a lot of time and effort, as you won’t need to fiddle around with each individual component.
- Improved Appearance
Another benefit of PCB assembly is that it can improve the appearance of your finished product. This is because all of the components are placed in the correct orientation and order, so they will all be perfectly aligned. This can give your product a professional and polished look.